New Hope for Heart Patients
Prof. Paul Santerre is working on a cardiac patch that would enable an injured heart to heal itself Read More
Prof. Paul Santerre is working on a cardiac patch that would enable an injured heart to heal itself Read More
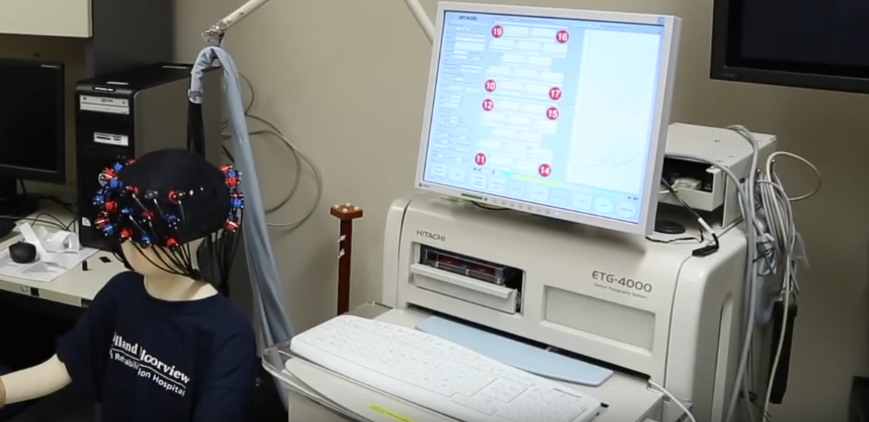
Prof. Tom Chau’s lab can already tell what word you’re thinking of, or if you’re singing a song to yourself Read More
Prof. Michael Sefton imagines being able to treat diabetes with a single injection Read More
U of T scientists will help usher in a new era of designing and creating cells, tissues and organs, thanks to historic $114-million federal grant Read More
Liver tissue created in a U of T lab could help reduce the time and cost of drug development Read More
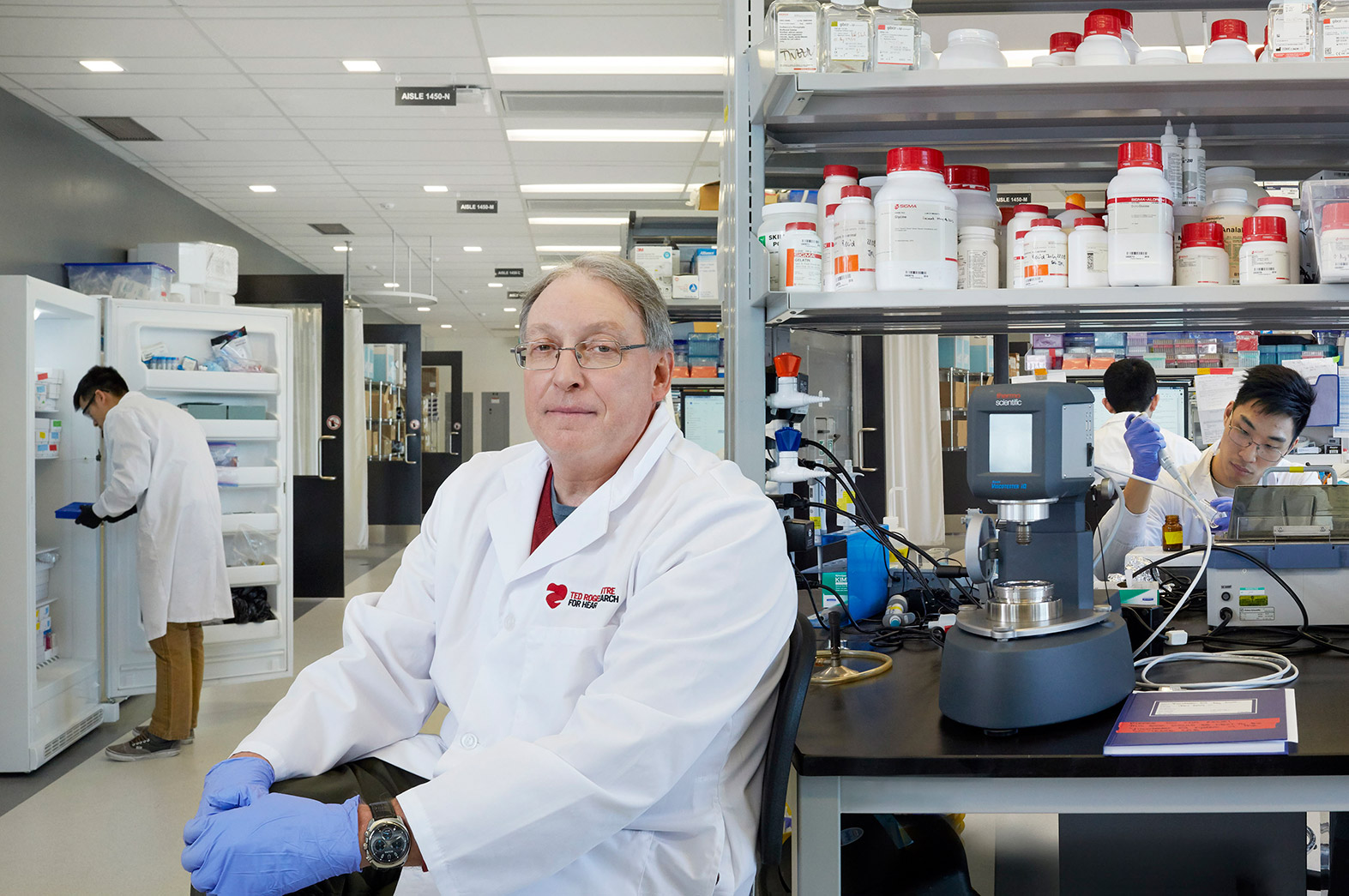
Largest private donation in Canadian health-care history will improve cardiac care across the lifespan Read More
The Ted Rogers Centre for Heart Research brings together three of Canada’s leading centres for cardiac care and research Read More
Recent grads win engineering design award for a low-cost medical device that will help keep patients breathing Read More
Leading scientist brought together experts from chemistry, medicine and dentistry to advance innovative new field Read More
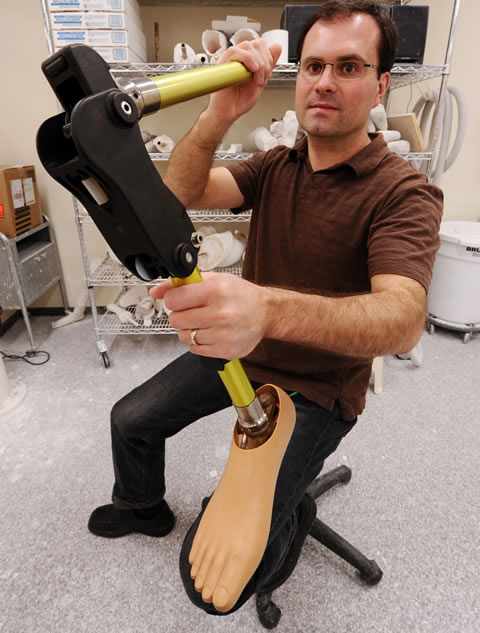
A new device promises to ease a major health concern for people with mobility problems Read More
Machine-made skin being developed at U of T may be safer, faster and cheaper than traditional grafts Read More
The simple, inexpensive device matches the function of far more costly technology Read More
Stem cell medicine may soon generate new treatments for any condition where cells have been damaged, such as heart disease, diabetes – even blindness Read More
Specially engineered tissue patches could help heart attack patients fully recover Read More
Portable device would offer hospitals a quicker way to test patients for infectious diseases Read More
After years of incremental progress, spinal cord repair is edging closer to reality Read More
Milligan gift will fund graduate fellowships in biomedical engineering Read More
Innovative treatment helps foster movement in arms and hands Read More
Procedure could help repair spinal cord injuries Read More
Technology's next big thing may be very, very small Read More
New development in bone growth may lead to new treatments Read More
Explore